HackerRank SQL
SQL 연습
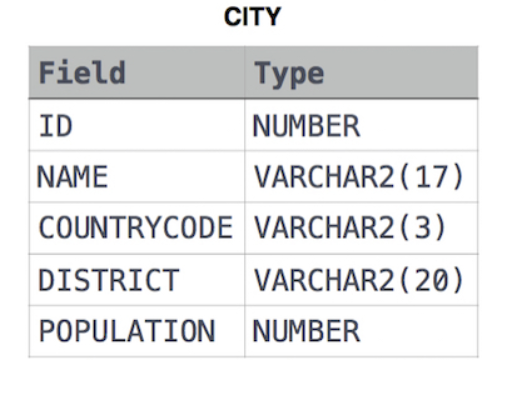
The CITY table is described as follows:
Revising the Select Query I
Query all columns for all American cities in the CITY table with populations larger than 100000. The CountryCode for America is USA.
1 | SELECT |
Revising the Select Query II
Query the NAME field for all American cities in the CITY table with populations larger than 120000. The CountryCode for America is USA.
1 | SELECT |
Select All
Query all columns (attributes) for every row in the CITY table.
1 | SELECT |
Select By ID
Query all columns for a city in CITY with the ID 1661.
1 | SELECT |
Japanese Cities’ Attributes
Query all attributes of every Japanese city in the CITY table. The COUNTRYCODE for Japan is JPN.
1 | SELECT |
Population Density Difference
Query the difference between the maximum and minimum populations in CITY.
1 | SELECT |
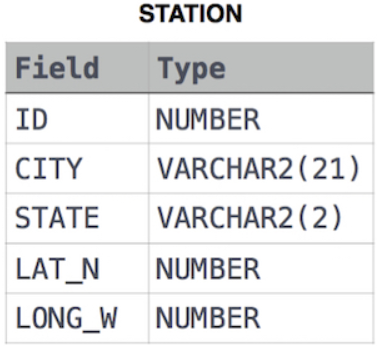
The STATION table is described as follows:
Weather Observation Station 1
Query a list of CITY and STATE from the STATION table.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 2
Query the following two values from the STATION table:
he sum of all values in LAT_N rounded to a scale of decimal places.
The sum of all values in LONG_W rounded to a scale of decimal places.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 3
Query a list of CITY names from STATION for cities that have an even ID number. Print the results in any order, but exclude duplicates from the answer.
even : 짝수
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 4
Find the difference between the total number of CITY entries in the table and the number of distinct CITY entries in the table.
1 |
|
Weather Observation Station 5
Query the two cities in STATION with the shortest and longest CITY names, as well as their respective lengths (i.e.: number of characters in the name). If there is more than one smallest or largest city, choose the one that comes first when ordered alphabetically.
1 | // 최댓값 |
Weather Observation Station 6
Query the list of CITY names starting with vowels (i.e., a, e, i, o, or u) from STATION. Your result cannot contain duplicates.
1 | SELECT |
SUBSTR(칼럼, index)
해당 칼럼을 index만큼 짤라서 리턴
Weather Observation Station 7
Query the list of CITY names ending with vowels (a, e, i, o, u) from STATION. Your result cannot contain duplicates.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 8
Query the list of CITY names from STATION which have vowels (i.e., a, e, i, o, and u) as both their first and last characters. Your result cannot contain duplicates.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 9
Query the list of CITY names from STATION that do not start with vowels. Your result cannot contain duplicates.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 10
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 11
Query the list of CITY names from STATION that either do not start with vowels or do not end with vowels. Your result cannot contain duplicates.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 12
Query the list of CITY names from STATION that do not start with vowels and do not end with vowels. Your result cannot contain duplicates.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 13
Query the sum of Northern Latitudes (LAT_N) from STATION having values greater than 37.7880 and less than 137.2345. Truncate your answer to 4 decimal places.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 14
Query the greatest value of the Northern Latitudes (LAT_N) from STATION that is less than . Truncate your answer to decimal places.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 15
Query the Western Longitude (LONG_W) for the largest Northern Latitude (LAT_N) in STATION that is less than 137,2345. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 16
Query the smallest Northern Latitude (LAT_N) from STATION that is greater than 38.7780. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.
1 | SELECT |
Weather Observation Station 17
Query the Western Longitude (LONG_W)where the smallest Northern Latitude (LAT_N) in STATION is greater than 38.7780. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.
1 | SELECT |
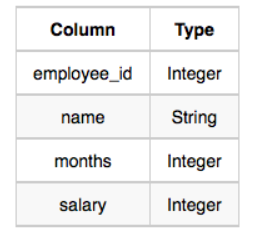
The EMPLOYEES table is described as follows:
Higher Than 75 Marks
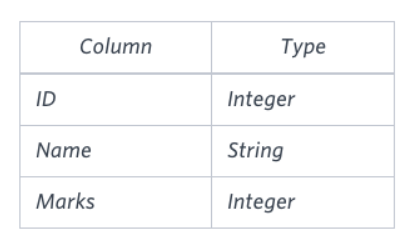
Query the Name of any student in STUDENTS who scored higher than Marks. Order your output by the last three characters of each name. If two or more students both have names ending in the same last three characters (i.e.: Bobby, Robby, etc.), secondary sort them by ascending ID.
1 | SELECT |
The Blunder
Samantha was tasked with calculating the average monthly salaries for all employees in the EMPLOYEES table, but did not realize her keyboard’s key was broken until after completing the calculation. She wants your help finding the difference between her miscalculation (using salaries with any zeroes removed), and the actual average salary.
Write a query calculating the amount of error (i.e.: average monthly salaries), and round it up to the next integer.
1 | SELECT |
The Employee table containing employee data for a company is described as follows:
Employee Names
Write a query that prints a list of employee names (i.e.: the name attribute) from the Employee table in alphabetical order.
1 | SELECT |
Employee Salaries
Write a query that prints a list of employee names (i.e.: the name attribute) for employees in Employee having a salary greater than per month who have been employees for less than months. Sort your result by ascending employee_id.
1 | SELECT |
TOP Earners
We define an employee’s total earnings to be their monthly salary * months worked, and the maximum total earnings to be the maximum total earnings for any employee in the Employee table. Write a query to find the maximum total earnings for all employees as well as the total number of employees who have maximum total earnings. Then print these values as space-separated integers.
1 | SELECT |
Print Prime Numbers
Write a query to print all prime numbers less than or equal to . Print your result on a single line, and use the ampersand () character as your separator (instead of a space).
For example, the output for all prime numbers would be:
1 | 2&3&5&7 |
1 | SELECT GROUP_CONCAT(NUMB SEPARATOR '&') |